What is an inguinal hernia?
An inguinal hernia is when part of the bowel pushes through a weakness in the groin called the inguinal canal.
What causes an inguinal hernia?
There are two types of inguinal hernia which have different causes and include:
Indirect inguinal hernia � is the most common type of inguinal hernia and is present at birth. This is more common in males and occurs when the entrance of the inguinal canal at the inguinal ring does not close as it should just after birth, leaving a weakness in the abdominal wall. Fat or part of the small intestine slides through the weakness into the inguinal canal, causing a hernia. Premature infants are especially at risk for indirect inguinal hernias because there is less time for the inguinal canal to close.
Direct inguinal hernia - is caused by connective tissue degeneration of the abdominal muscles in men, which causes weakening of the muscles resulting in fat or the small intestine sliding through the weak muscles into the groin. A direct hernia develops gradually because of continuous stress on the abdominal during activities such as:
- sudden twists, pulls, or muscle strains
- lifting heavy objects
- straining on the toilet because of constipation
- weight gain
- chronic coughing
What are the symptoms/effects of an inguinal hernia?
Symptoms of an inguinal hernia include
- A small bulge in one or both sides of the groin that may increase in size and disappear when lying down. This may also present as a swollen or enlarged scrotum in men.
- Pain when straining, lifting, or exercising
- A feeling of weakness or pressure in the groin
- A burning, or aching feeling at the bulge
Diagnosis of an inguinal hernia
To diagnose an inguinal hernia, a physiotherapist or a doctor will take a thorough medical history and physical examination.
Treatment for an inguinal hernia
Inguinal hernias are usually treated with surgery to push the bulge back into place and repair the hernia. This may involve an open procedure or laparoscopy (key hole surgery) depending on your current symptoms.
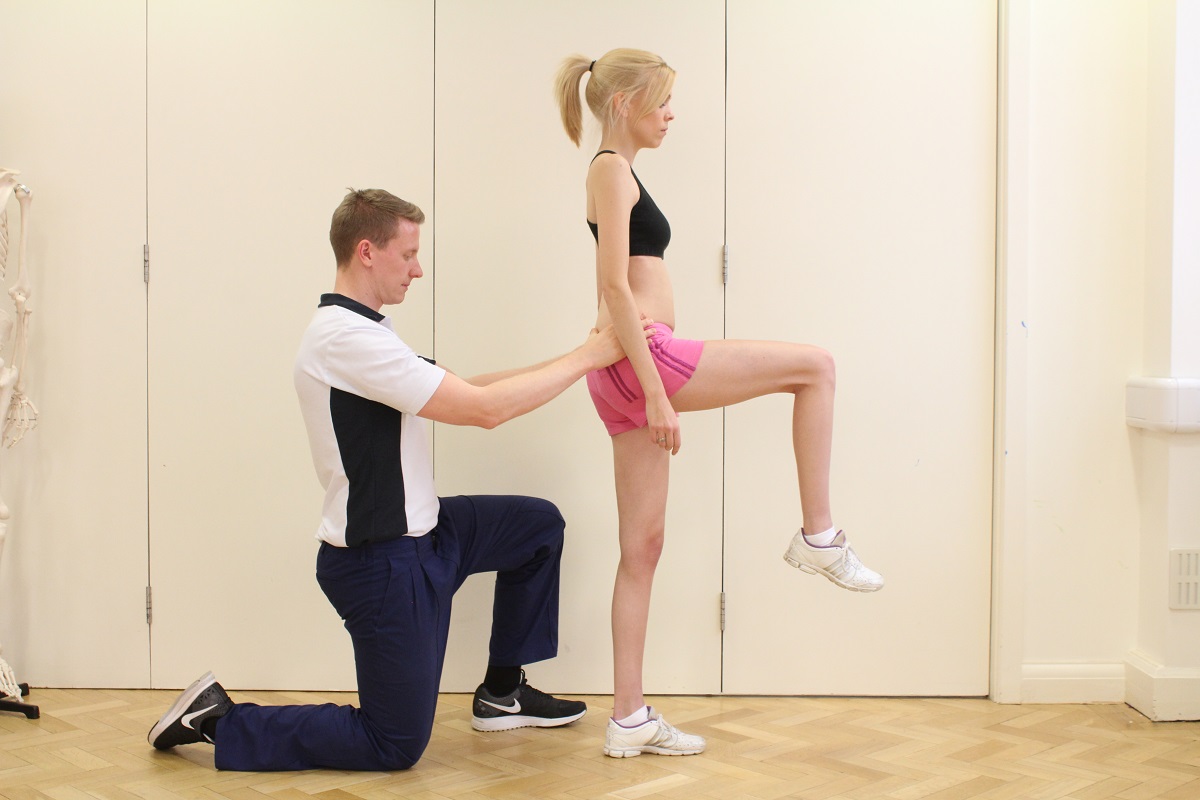
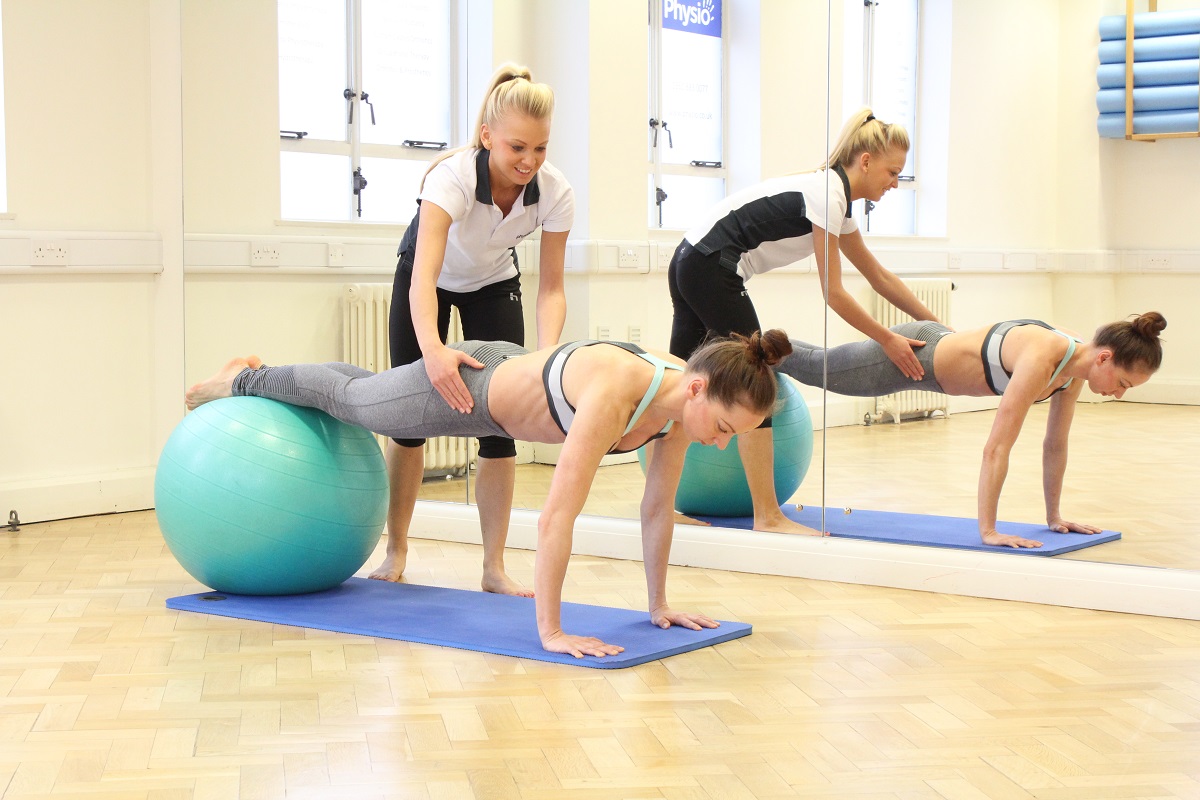
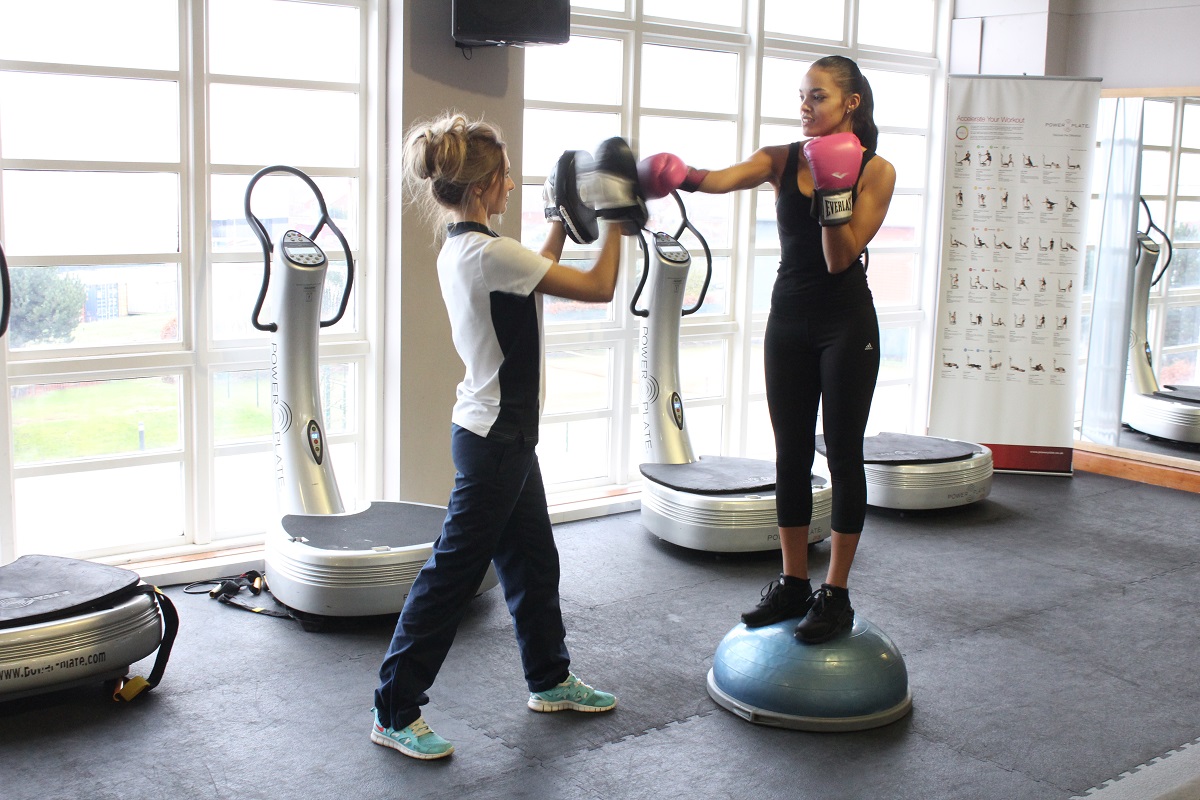
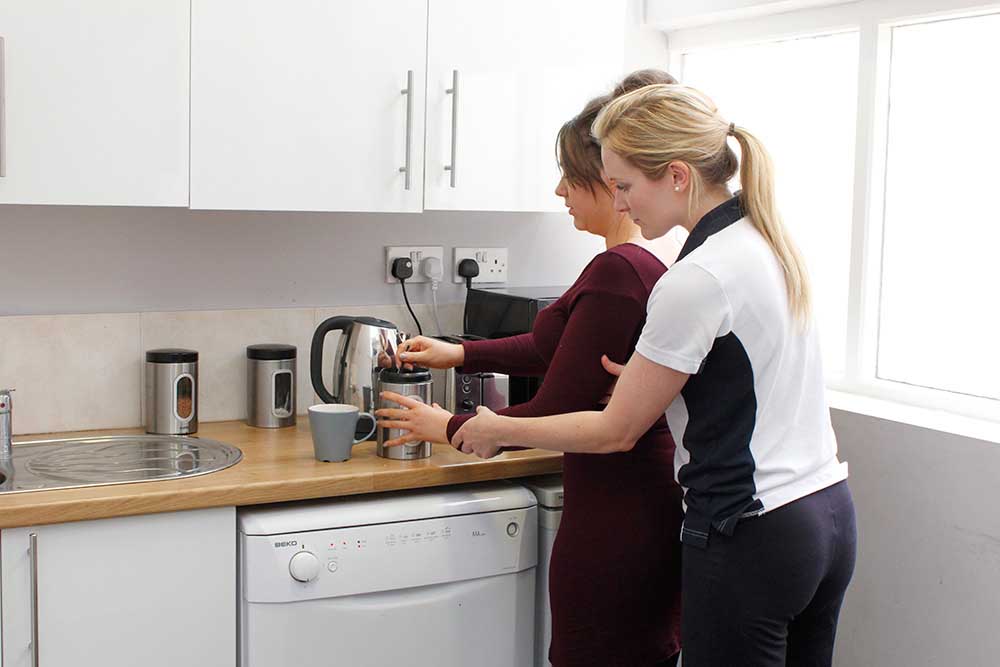
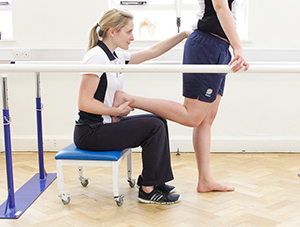
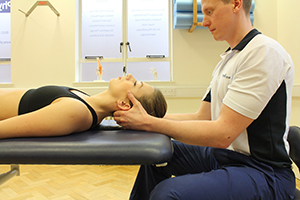
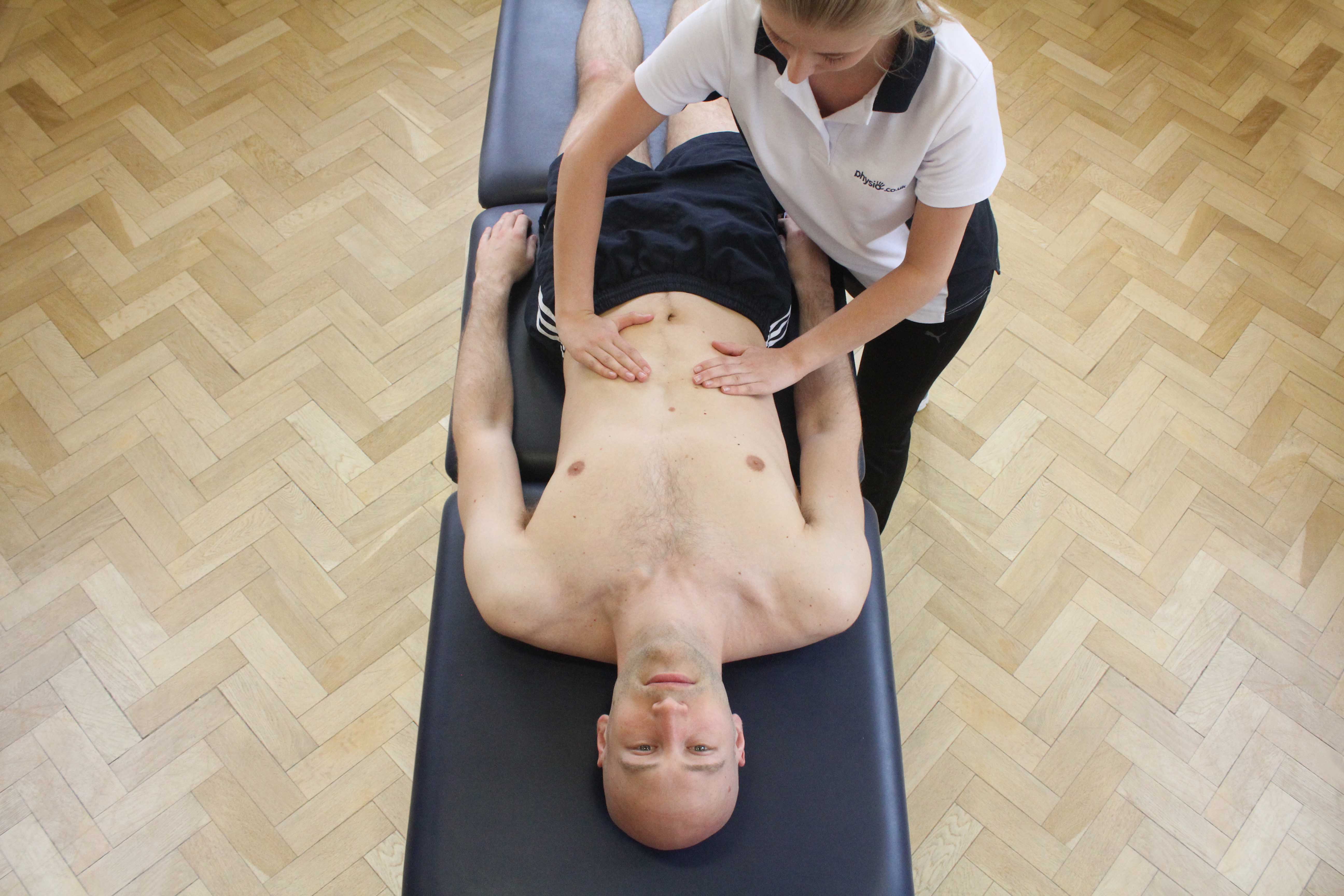
Physiotherapy following surgery for inguinal hernia
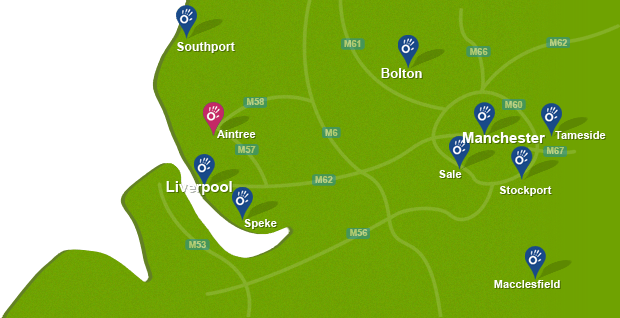
Our physiotherapists at Manchester Physio provide specialised physiotherapy treatment following your operation.
Physiotherapy treatment at Manchester Physio will shorten your recovery time and advise you on the type of exercises that should be started and when, to ensure you get back to your everyday activities safely and effectively.
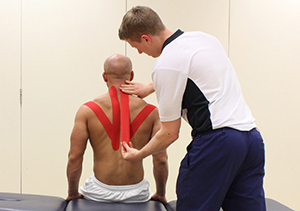
Physiotherapy treatment will be tailored to you but may include:
- Advice on what activity to avoid
- Advice on how to modify activity
- Ice or heat therapy to reduce pain
- Ultrasound to accelerate healing
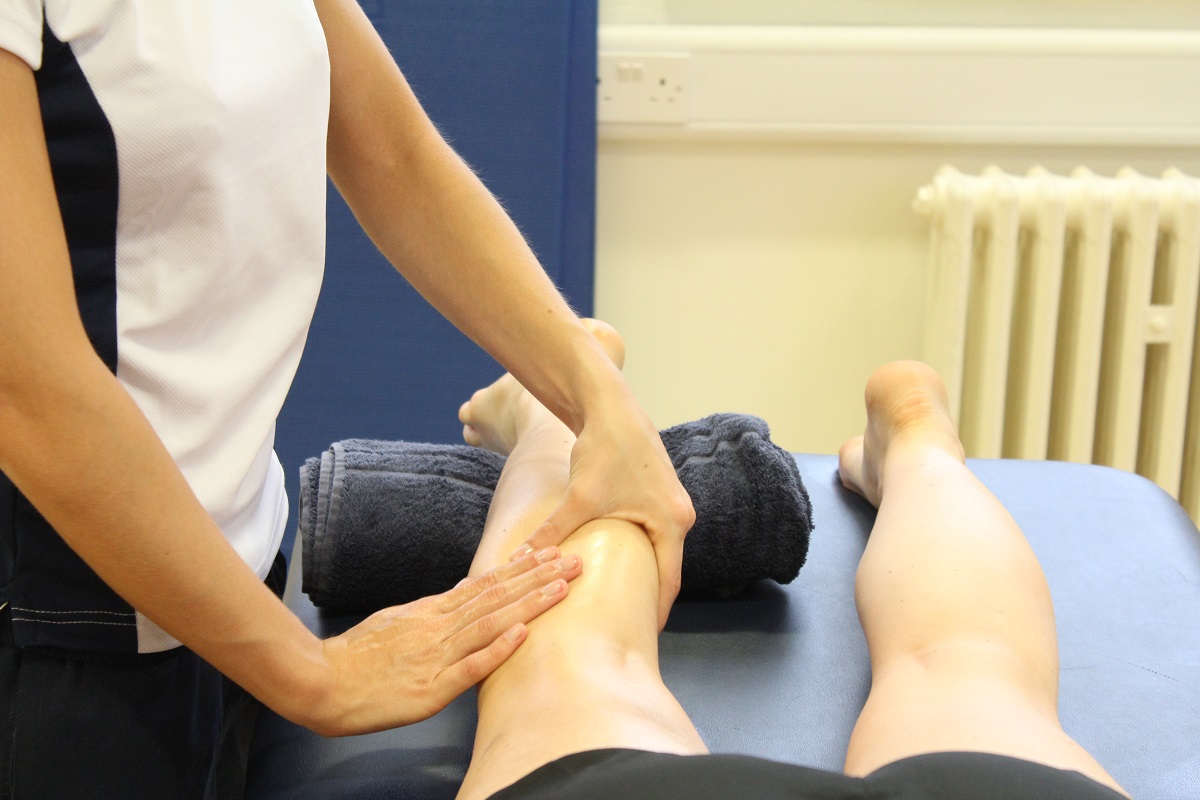
- Soft tissue massage to lengthen tight muscles
- Stretching and abdominal strengthening exercises at the right time, to regain range of movement and strength.
- Gradual return to sport and daily tasks
Physiotherapy treatment at Manchester Physio will relieve pain and discomfort and regain muscle strength and length following your operation, so that you can safely return to work and sport as soon as possible.
For more information as to whether you would benefit from physiotherapy, or to book an appointment please call 0161 883 0077.



 0161 883 0077
0161 883 0077










 Above: filetitle1
Above: filetitle1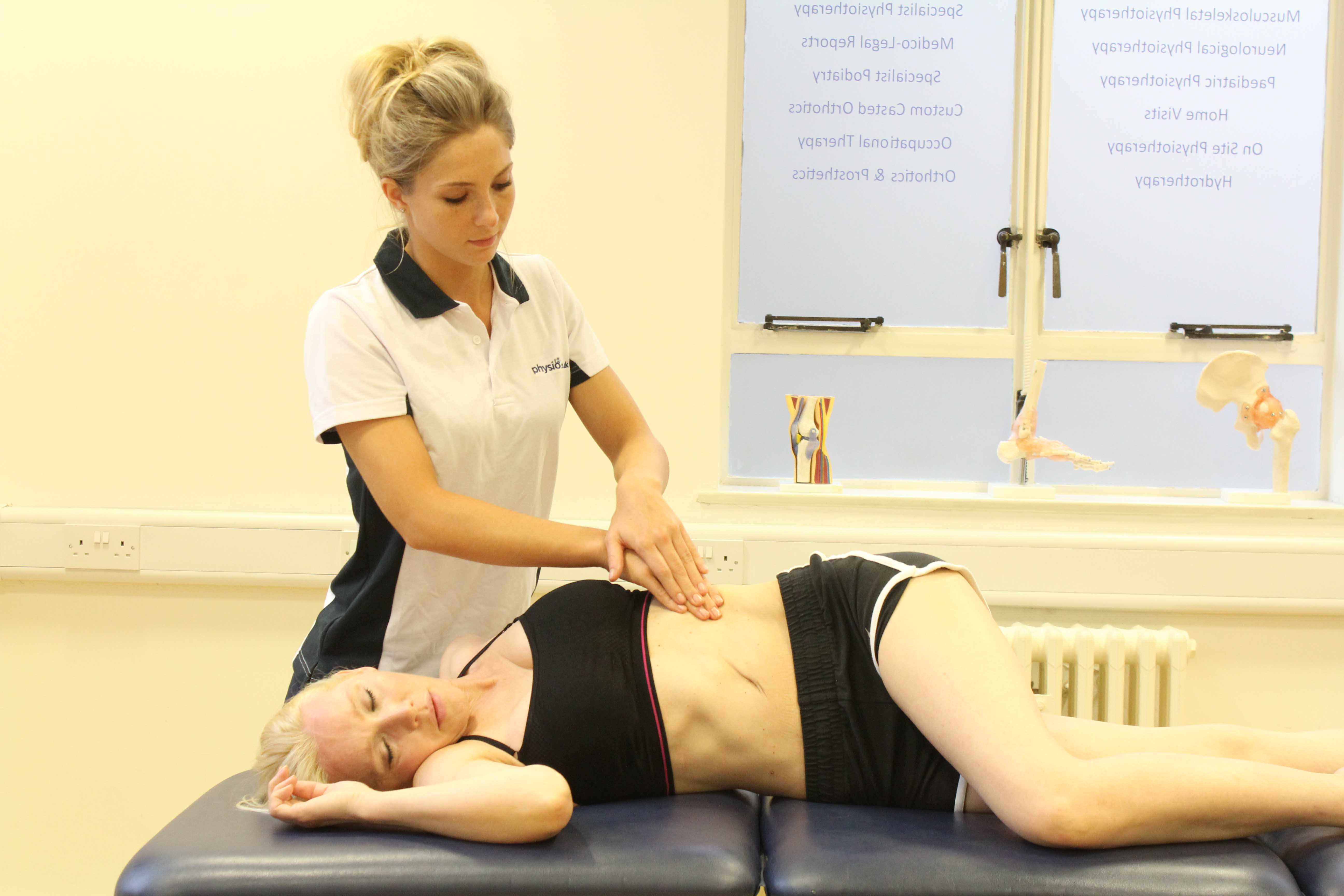 Above: filetitle2
Above: filetitle2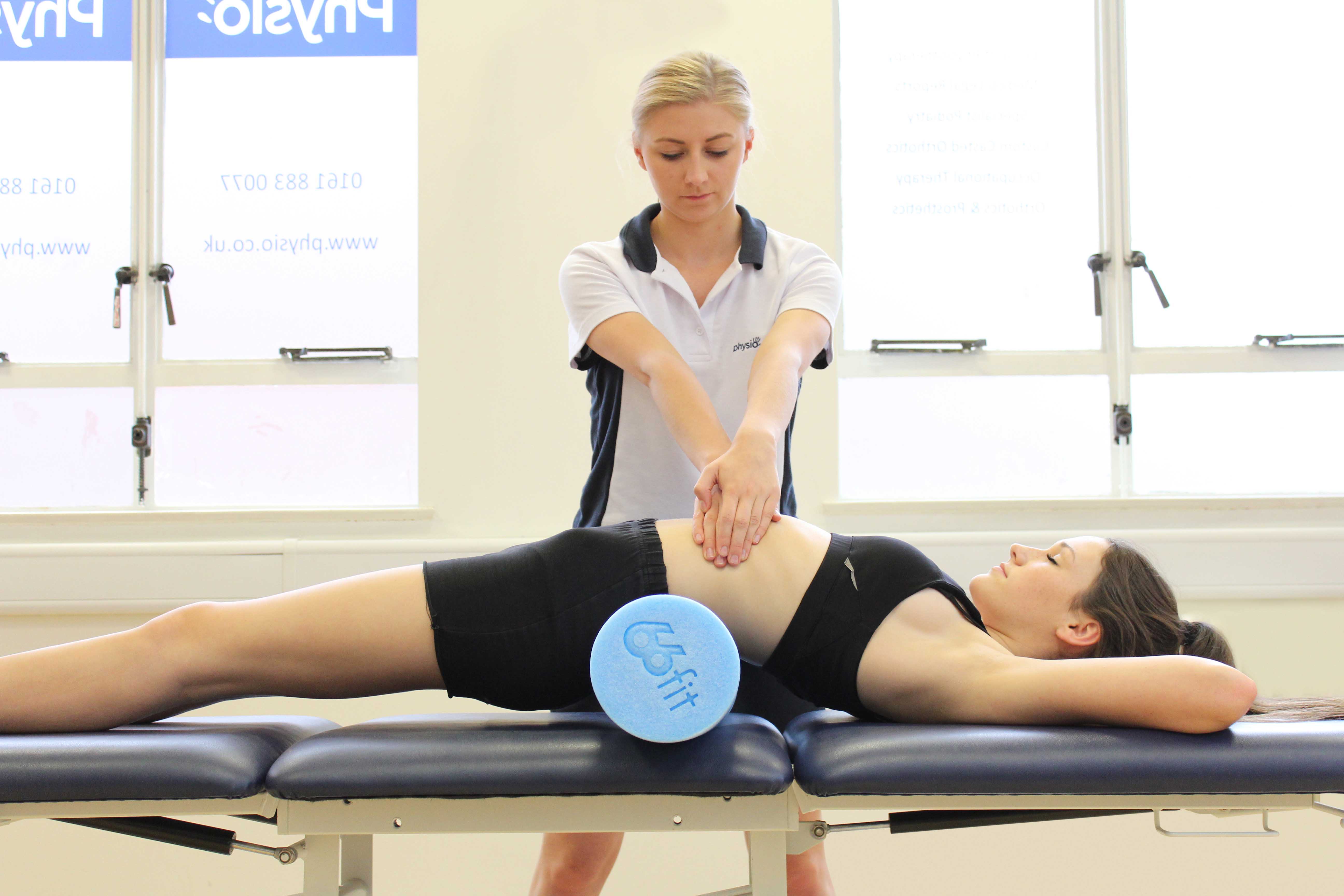 Above: filetitle3
Above: filetitle3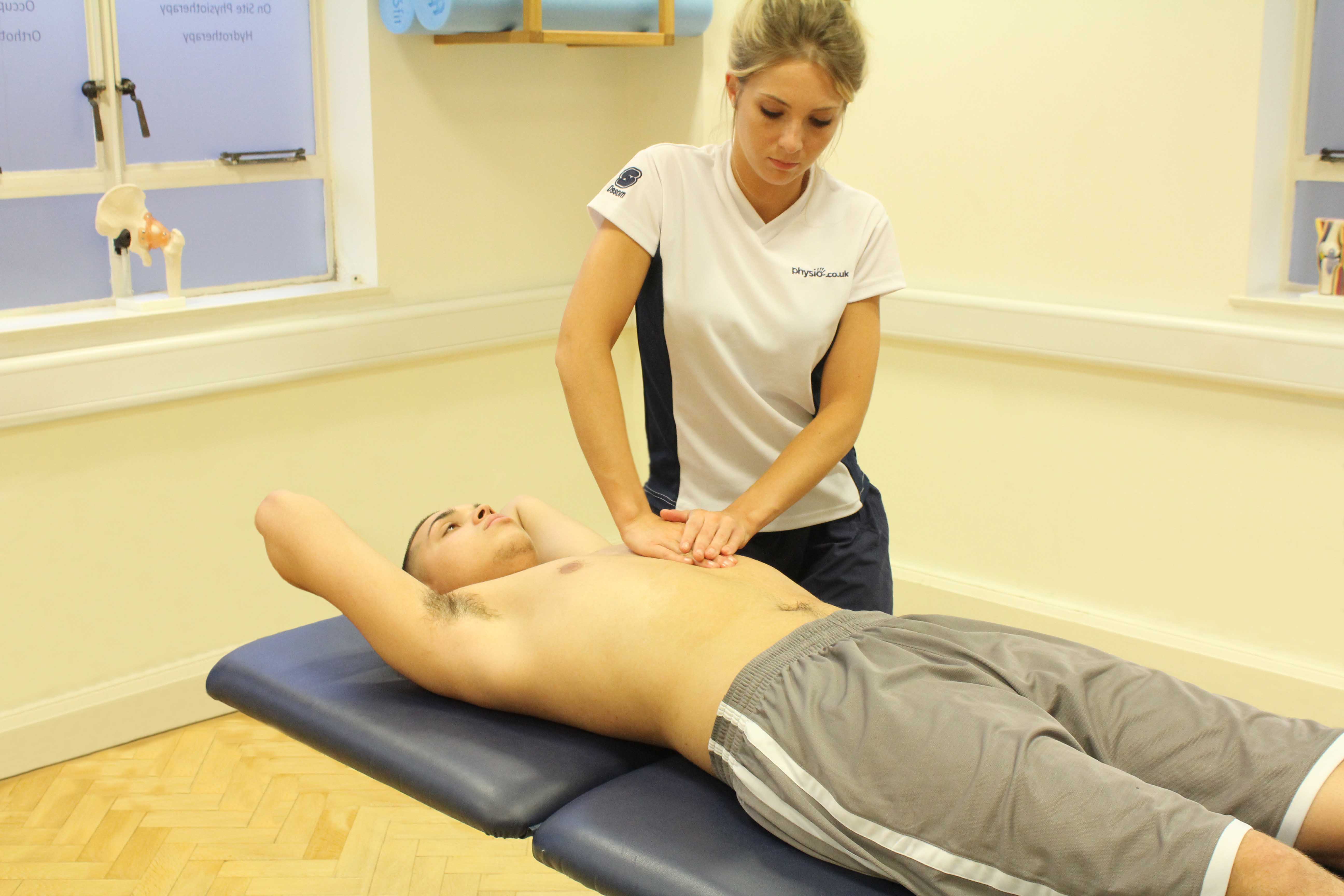 Above: filetitle4
Above: filetitle4





















 f
f